¶ GPIO编程
Linux GPIO 通过sysfs 方式进行操控, 进入到/sys/class/gpio 目录下。
export:用于将指定编号的GPIO 引脚导出。在使用GPIO 引脚之前,需要将其导出,导出成功之后才能使用它。
unexport:将导出的GPIO 引脚删除。当使用完GPIO 引脚之后,我们需要将导出的引脚删除。
将指定的编号写入到export 文件中,可以导出指定编号的GPIO 引脚,导出成功之后会在/sys/class/gpio目录下生成对应的gpioX(X 表示GPIO 的编号)。
direction:配置GPIO 引脚为输入或输出模式。该文件可读、可写,读表示查看GPIO 当前是输入还是输出模式,写表示将GPIO 配置为输入或输出模式;读取或写入操作可取的值为"out"(输出模式)和"in"(输入模式)。
value:在GPIO 配置为输出模式下,向value 文件写入"0"控制GPIO 引脚输出低电平,写入"1"则控制GPIO 引脚输出高电平。在输入模式下,读取value 文件获取GPIO 引脚当前的输入电平状态。
active_low:这个属性文件用于控制极性,可读可写。
edge:控制中断的触发模式,该文件可读可写。在配置GPIO 引脚的中断触发模式之前,需将其设置为输入模式:
非中断引脚:echo “none” > edge
上升沿触发:echo “rising” > edge
下降沿触发:echo “falling” > edge
边沿触发:echo “both” > edge
瑞芯微GPIO对应用户空间的gpio编号如下表。
| GPIO | GPIO编号 |
|---|---|
| GPIO0_B0 | 8 |
| GPIO2_C0 | 80 |
| GPIO4_C3 | 147 |
| GPIO0_C5 | 21 |
| GPIO4_C4 | 148 |
| GPIO4_C5 | 149 |
| GPIO2_B2 | 74 |
| GPIO2_B1 | 73 |
¶ 配置GPIO输出
cd /sys/class/gpio/
# 将文件用于者改为youyeetoo
sudo chown youyeetoo:youyeetoo export
sudo chown youyeetoo:youyeetoo unexport
# 以GPIO0_B0为例操作gpio输出,其他gpio操作只需要根据上一个表格的对应关系导出即可。
# 导出 GPIO0_B0
echo 8 > export
# 将文件用于者改为youyeetoo
sudo chown youyeetoo:youyeetoo gpio8/direction
sudo chown youyeetoo:youyeetoo gpio8/value
cd gpio8
# 设置输出
echo out > direction
# 输出高电平
echo 1 > value
# 输出低电平
echo 0 > value
# 删除导出gpio引脚
cd ..
echo 8 > unexport
vim gpio_output.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
static char gpio_path[32];
static int gpio_config(const char *attr, const char *val)
{
char file_path[64];
int len;
int fd;
sprintf(file_path, "%s/%s", gpio_path, attr);
fd = open(file_path, O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open error");
return fd;
}
len = strlen(val);
if (len != write(fd, val, len)) {
perror("write error");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
close(fd); //关闭文件
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int fd;
int len;
/* 校验传参 */
if (argc != 3) {
fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s <gpio> <value>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 判断指定编号的GPIO是否导出 */
sprintf(gpio_path, "/sys/class/gpio/gpio%s", argv[1]);
if (access(gpio_path, F_OK)) {//如果目录不存在 则需要导出
fd = open("/sys/class/gpio/export", O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
len = strlen(argv[1]);
if (len != write(fd, argv[1], len)) {//导出gpio
perror("write error");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
close(fd); //关闭文件
}
/* 配置为输出模式 */
if (gpio_config("direction", "out")) return -1;
/* 极性设置 */
if (gpio_config("active_low", "0")) return -1;
/* 控制GPIO输出高低电平 */
if (gpio_config("value", argv[2])) return -1;
close(fd);
/* 退出程序 */
return 0;
}
gcc gpio_output.c -o gpio_output
# 输出高电平
sudo ./gpio_output 8 1
# 输出低电平
sudo ./gpio_output 8 0
¶ 配置GPIO输入
cd /sys/class/gpio/
# 将文件用于者改为youyeetoo
sudo chown youyeetoo:youyeetoo export
sudo chown youyeetoo:youyeetoo unexport
# 以GPIO0_B0为例操作gpio输出,其他gpio操作只需要根据上一个表格的对应关系导出即可。
# 导出 GPIO0_B0
echo 8 > export
# 将文件用于者改为youyeetoo
sudo chown youyeetoo:youyeetoo gpio8/direction
sudo chown youyeetoo:youyeetoo gpio8/value
cd gpio8
# 设置输出
echo in > direction
# 查看gpio电平
cat value
# 删除导出gpio引脚
cd ..
echo 8 > unexport
vim gpio_input.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
static char gpio_path[32];
static int gpio_config(const char *attr, const char *val)
{
char file_path[64];
int len;
int fd;
sprintf(file_path, "%s/%s", gpio_path, attr);
if (0 > (fd = open(file_path, O_WRONLY))) {
perror("open error");
return fd;
}
len = strlen(val);
if (len != write(fd, val, len)) {
perror("write error");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
close(fd); //关闭文件
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char file_path[64];
char val;
int fd;
int len;
/* 校验传参 */
if (argc != 2) {
fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s <gpio>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 判断指定编号的GPIO是否导出 */
sprintf(gpio_path, "/sys/class/gpio/gpio%s", argv[1]);
if (access(gpio_path, F_OK)) {//如果目录不存在 则需要导出
if ((fd = open("/sys/class/gpio/export", O_WRONLY)) < 0) {
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
len = strlen(argv[1]);
if (len != write(fd, argv[1], len)) {//导出gpio
perror("write error");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
close(fd); //关闭文件
}
/* 配置为输入模式 */
if (gpio_config("direction", "in")) return -1;
/* 极性设置 */
if (gpio_config("active_low", "0")) return -1;
/* 配置为非中断方式 */
if (gpio_config("edge", "none")) return -1;
/* 读取GPIO电平状态 */
sprintf(file_path, "%s/%s", gpio_path, "value");
if ((fd = open(file_path, O_RDONLY)) < 0) {
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
if (read(fd, &val, 1) < 0) {
perror("read error");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
printf("value: %c\n", val);
/* 退出程序 */
close(fd);
return 0;
}
编译运行,读取gpio管脚电平
gcc gpio_input.c -o gpio_input
sudo ./gpio_input 8
¶ 配置GPIO中断
vim gpio_irq.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <poll.h>
static char gpio_path[32];
static int gpio_config(const char *attr, const char *val)
{
char file_path[64];
int len;
int fd;
sprintf(file_path, "%s/%s", gpio_path, attr);
fd = open(file_path, O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open error");
return fd;
}
len = strlen(val);
if (len != write(fd, val, len)) {
perror("write error");
return -1;
}
close(fd); //关闭文件
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct pollfd pfd;
char file_path[64];
int ret;
char val;
int len;
int fd;
/* 校验传参 */
if (argc != 2) {
fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s <gpio>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 判断指定编号的GPIO是否导出 */
sprintf(gpio_path, "/sys/class/gpio/gpio%s", argv[1]);
if (access(gpio_path, F_OK)) {//如果目录不存在 则需要导出
fd = open("/sys/class/gpio/export", O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
len = strlen(argv[1]);
if (len != write(fd, argv[1], len)) {//导出gpio
perror("write error");
return -1;
}
close(fd); //关闭文件
}
/* 配置为输入模式 */
if (gpio_config("direction", "in")) return -1;
/* 极性设置 */
if (gpio_config("active_low", "0")) return -1;
/* 配置中断触发方式: 上升沿和下降沿 */
if (gpio_config("edge", "both")) return -1;
/* 打开value属性文件 */
sprintf(file_path, "%s/%s", gpio_path, "value");
pfd.fd = open(file_path, O_RDONLY);
if (pfd.fd < 0) {
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
/* 调用poll */
pfd.events = POLLPRI; //只关心高优先级数据可读(中断)
read(pfd.fd, &val, 1);//先读取一次清除状态
while (1) {
ret = poll(&pfd, 1, -1); //调用poll
if (ret < 0) {
perror("poll error");
return -1;
} else if (ret == 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "poll timeout.\n");
continue;
} else {
/* 校验高优先级数据是否可读 */
if(pfd.revents & POLLPRI) {
if (lseek(pfd.fd, 0, SEEK_SET) < 0) {//将读位置移动到头部
perror("lseek error");
return -1;
}
if (read(pfd.fd, &val, 1) < 0) {
perror("read error");
return -1;
}
printf("GPIO Interrupt Trigger <value=%c>\n", val);
}
}
}
/* 退出程序 */
return 0;
}
编译运行
gcc gpio_irq.c -o gpio_irq
sudo ./gpio_irq
¶ Uart编程
串口通信是一种重要的设备通信方式,它通过串行方式在设备之间传输数据。在Linux系统中,串口设备被抽象为特殊的文件,位于/dev目录下,常见的串口设备文件如/dev/ttyS0、/dev/ttyS1(传统串口)或/dev/ttyUSB0、/dev/ttyACM0(USB转串口设备)。在串口通信中需要配置以下核心参数。
串口通信的核心参数包括:
- 波特率(Baud Rate):数据传输速率,常见的有9600、19200、38400、57600、115200等
- 数据位(Data Bits):每个数据帧中实际包含的数据位数,通常为5-8位
- 停止位(Stop Bits):用于表示数据帧结束的位数,通常为1或2位
- 校验位(Parity Bit):用于简单的错误检测,可以是无校验(None)、奇校验(Odd)或偶校验(Even)
- 流控制(Flow Control):用于控制数据传输速率,可以是无流控制(None)、软件流控制(XON/XOFF)或硬件流控制(RTS/CTS)
YY3588开发板一共提供4个uart供客户使用,分别注册为ttyS1、ttyS6、ttyS7、ttyS9,对应硬件位置请查看原理图。串口使用可以使用shell方式或者编程语言读写配置方式。本文只介绍shell方式和c语言方式。
- 在开发板上查看串口配置,默认情况下,串口的波特率为9600。
sudo stty -F /dev/ttyS1 -a
- 连接串口
板子的TX接到串口模块的RX上,板子的RX接到串口模块的TX上,再接板子的GND到串口模块的GND上。然后将串口模块连接到电脑上。
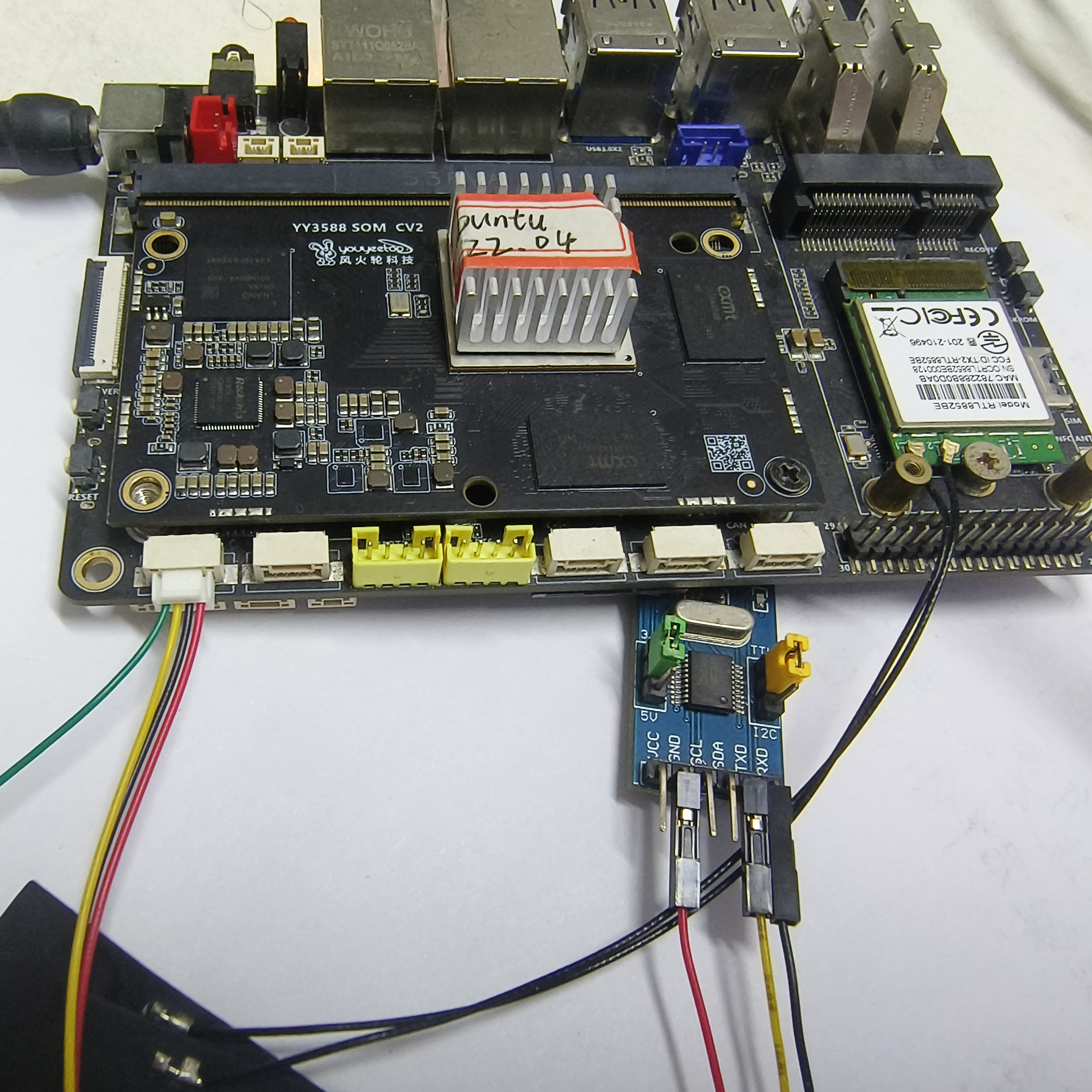
-
在电脑上打开串口软件,在串口软件配置默认的9600即可完成通信。
-
在开发板上输入以下命令接受发送过来的串口数据
sudo chmod 666 /dev/ttyS1
cat /dev/ttyS1
- 开发板发送串口数据命令
sudo chmod 666 /dev/ttyS1
echo "Serial information to be sent" > /dev/ttyS1
- 如果需要修改波特率、数据位等配置,执行以下命令。
# 设置/dev/ttyS1串口波特率为115200
sudo stty -F /dev/ttyS1 speed 115200
# 设置数据位,如设置8位数据位参数为cs8,7位数据位为cs7
sudo stty -F /dev/ttyS1 cs8
# 停止位用于标识一个字符传输的结束。通常使用 1 或 2 个停止位。1位停止位参数为cstopb,2位停止位为-cstopb
sudo stty -F /dev/ttyS1 cstopb
# 设置奇校验:
sudo stty -F /dev/ttyS1 parenb parodd
# 设置为偶校验:
sudo stty -F /dev/ttyS1 parenb -parodd
# 关闭校验:
sudo stty -F /dev/ttyS1 -parenb
- 电脑上的串口软件也要设置跟开发板上的串口参数一致,即可完成串口通信。

Linux环境下进行C语言串口编程通常包括以下基本步骤:
- 打开串口设备:使用open()函数打开串口设备文件
- 配置串口参数:使用tcgetattr()和tcsetattr()函数配置串口参数
- 读写数据:使用read()和write()函数进行数据收发
- 关闭串口设备:使用close()函数关闭串口设备
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int configure_serial_port(const char *device, int baud_rate)
{
int serial_port;
serial_port = open(device, O_RDWR);
if (serial_port < 0) {
printf("Error %i opening %s: %s\n", errno, device, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
struct termios tty;
memset(&tty, 0, sizeof tty);
if (tcgetattr(serial_port, &tty) != 0) {
printf("Error %i from tcgetattr: %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
close(serial_port);
return -1;
}
// 设置波特率
cfsetospeed(&tty, baud_rate);
cfsetispeed(&tty, baud_rate);
// 设置8N1模式:8位数据位,无校验位,1位停止位
tty.c_cflag &= ~PARENB; // 无校验位
tty.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB; // 1位停止位
tty.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE; // 清除数据位设置
tty.c_cflag |= CS8; // 8位数据位
// 禁用硬件流控制
tty.c_cflag &= ~CRTSCTS;
// 启用接收,忽略调制解调器控制线
tty.c_cflag |= CREAD | CLOCAL;
// 禁用软件流控制
tty.c_iflag &= ~(IXON | IXOFF | IXANY);
// 原始输入模式
tty.c_lflag &= ~(ICANON | ECHO | ECHOE | ISIG);
// 原始输出模式
tty.c_oflag &= ~OPOST;
// 设置超时和最小读取字符数
tty.c_cc[VMIN] = 1; // 至少读取1个字符
tty.c_cc[VTIME] = 1; // 等待字符的超时时间为0.1秒
// 保存设置
if (tcsetattr(serial_port, TCSANOW, &tty) != 0) {
printf("Error %i from tcsetattr: %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
close(serial_port);
return -1;
}
return serial_port;
}
int main()
{
const char *device = "/dev/ttyS1";
int baud_rate = B9600;
// 配置串口
int serial_port = configure_serial_port(device, baud_rate);
if (serial_port < 0) {
return 1;
}
// 写入数据
const char *message = "Hello, Serial Port!";
ssize_t bytes_written = write(serial_port, message, strlen(message));
if (bytes_written < 0) {
printf("Error writing to serial port: %s\n", strerror(errno));
close(serial_port);
return 1;
}
printf("Written %zd bytes: %s\n", bytes_written, message);
// 读取数据
unsigned char buffer[256];
ssize_t bytes_read = read(serial_port, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1);
if (bytes_read < 0) {
printf("Error reading from serial port: %s\n", strerror(errno));
close(serial_port);
return 1;
}
// 确保字符串以null结尾
buffer[bytes_read] = '\0';
printf("Read %zd bytes: %s\n", bytes_read, buffer);
// 关闭串口
close(serial_port);
return 0;
}
c程序编译运行,参考shell方式连接好串口。
sudo chmod 666 /dev/ttyS1
gcc serial.c -o serial
sudo ./serial
¶ I2C编程
Linux 环境下,有多种工具可以帮助用户与 I2C 设备进行交互。其中最常用的工具是 i2c-tools 包中提供的命令行工具,包括 i2cdetect、i2cset 和 i2cget 等。
- 安装i2c-tools工具
sudo apt-get install i2c-tools
- 查看i2c6总线上挂载设备
sudo i2cdetect -y 6
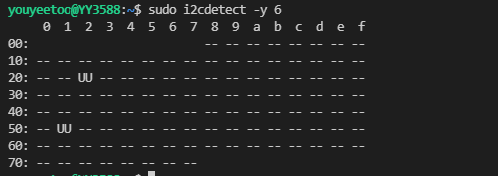
-
上图中地址为0x51有一个设备,该设备为 hym8563即RTC。本文以RTC为例讲解i2c读写。
-
读取命令格式
sudo i2cget -y -f i2c总线号 从机地址 寄存器
- hym8563的 月/世纪寄存器(地址07H)位描述
| 位号 | 符号 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 7 | C | 世纪位:C=0指定世纪数为20XX;C=1指定世纪数为19XX,“XX”为年寄存器中的值 |
| 6,5 | - | 无效 |
| 4~0 | 月 | 代表BCD格式的当前月份数值,值为01~12 |
- hym8563的年寄存器(地址08H)位描述
| 位号 | 符号 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 7~0 | 年 | 代表BCD格式的当前年数值,值为00~99 |
读取月/世纪寄存器和年寄存器命令如下
# 读取月/世纪寄存器
sudo i2cget -y -f 6 0x51 0x07
# 读取年寄存器
sudo i2cget -y -f 6 0x51 0x08
# 查看RTC时间
sudo hwclock -r
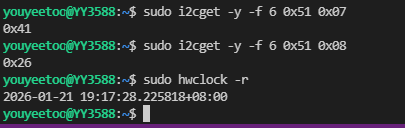
读出月/世纪寄存器值为0x41,换算成二进制为01000001,得出C=0,即世纪为20,月份为1月,年寄存器寄存器值为0x26,换算成BCD码格式为26。即读出的年月为2026-01,与hwclock命令读出的年月一致。
- 写入命令格式
sudo i2cset -y -f i2c总线号 从机地址 寄存器 值
如设置RTC时钟年月为2027-02,命令如下
# 设置月/世纪寄存器
sudo i2cset -y -f 6 0x51 0x07 0x42
# 设置年寄存器
sudo i2cset -y -f 6 0x51 0x08 0x27
# 查看RTC时间
sudo hwclock -r
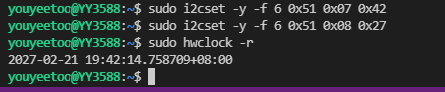
本c程序以RTC为例进行i2c读写。相关从机地址和寄存器介绍看shell方式。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <linux/i2c-dev.h>
#include <linux/i2c.h>
/* RTC所对应的I2C控制器的设备节点 */
#define RTC_DEVICE "/dev/i2c-6"
/* RTC的I2C设备地址 */
#define RTC_ADDR 0x51
int i2c_write(int fd, unsigned char dev_addr, unsigned char reg_addr, unsigned char* data_buf, int len)
{
int ret;
unsigned char msg_buf[9];
struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data data;
struct i2c_msg messages;
msg_buf[0] = reg_addr;
if (len < 9) {
memcpy((void *) &msg_buf[1], data_buf, len);
} else {
printf("This function supports up to 8 bytes at a time !!!\n");
return -1;
}
messages.addr = dev_addr;
messages.flags = 0;
messages.len = len + 1;
messages.buf = msg_buf;
data.msgs = &messages;
data.nmsgs = 1;
if(ioctl(fd, I2C_RDWR, &data) < 0) {
printf("I2C_RDWR err \n");
return -1;
}
sleep(1);
return 0;
}
int i2c_read(int fd, unsigned char dev_addr, unsigned char reg_addr, unsigned char* data_buf, int len)
{
int ret;
struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data data;
struct i2c_msg messages[2];
messages[0].addr = dev_addr;
messages[0].flags = 0;
messages[0].len = 1;
messages[0].buf = ®_addr;
messages[1].addr = dev_addr;
messages[1].flags = I2C_M_RD;
messages[1].len = len;
messages[1].buf = data_buf;
data.msgs = messages;
data.nmsgs = 2;
if(ioctl(fd, I2C_RDWR, &data) < 0) {
printf("I2C_RDWR err \n");
return -1;
}
sleep(1);
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int fd;
unsigned char reg=0x07;
unsigned char rd_buf[2] = {0};
unsigned char wr_buf[2] = {0x42, 0x27};
fd = open(RTC_DEVICE, O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0) {
printf("open"RTC_DEVICE"failed \n");
return -1;
}
i2c_read(fd, RTC_ADDR, reg, rd_buf, 2);
printf("read reg(0x07): 0x%02x\n", rd_buf[0]);
printf("read reg(0x08): 0x%02x\n", rd_buf[1]);
i2c_write(fd, RTC_ADDR, reg, wr_buf, 2);
i2c_read(fd, RTC_ADDR, reg, rd_buf, 2);
printf("write reg(0x07): 0x%02x\n", rd_buf[0]);
printf("write reg(0x08): 0x%02x\n", rd_buf[1]);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
c程序编译运行。
gcc i2c_test.c -o i2c_test
sudo ./i2c_test
¶ CAN
- 安装can工具
sudo apt-get install can-utils
- 查看can节点
ifconfig -a
- 设置can节点
sudo ifconfig can0 down
sudo ip link set can0 type can bitrate 500000 triple-sampling on
# 如果没有can设备进行测试,可以使用以下命令设置can为回环测试。
sudo ip link set can0 type can loopback on
sudo ifconfig can0 up
- 查看can节点状态
sudo ip -details link show can0
- 打开两个终端接口(一个用来查看、一个用来发送)
- 发送接收can消息
sudo cansend can0 123#000102030405060708
- 接收消息
sudo candump can0
can通信流程
- 打开套接字
- 指定通信设备
- 将通信设备和套接字绑定
- 设置过滤规则
- 循环接收发送过来的数据(校验是否接收到错误帧、校验帧格式、校验帧类型、打印数据)
- 关闭套接字
- CAN发送应用程序示例
/* 1. 报文发送程序 */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <net/if.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <linux/can.h>
#include <linux/can/raw.h>
int main()
{
int s, nbytes;
struct sockaddr_can addr;
struct ifreq ifr;
struct can_frame frame[2] = {{0}};
s = socket(PF_CAN, SOCK_RAW, CAN_RAW);//创建套接字
strcpy(ifr.ifr_name, "can0" );
ioctl(s, SIOCGIFINDEX, &ifr); //指定 can0 设备
addr.can_family = AF_CAN;
addr.can_ifindex = ifr.ifr_ifindex;
bind(s, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, sizeof(addr));//将套接字与 can0 绑定
//禁用过滤规则,本进程不接收报文,只负责发送
setsockopt(s, SOL_CAN_RAW, CAN_RAW_FILTER, NULL, 0);
//生成两个报文
frame[0].can_id = 0x11;
frame[0]. can_dlc = 1;
frame[0].data[0] = 'Y';
frame[1].can_id = 0x22;
frame[1]. can_dlc = 1;
frame[1].data[0] = 'N';
//循环发送两个报文
while(1)
{
nbytes = write(s, &frame[0], sizeof(frame[0])); //发送 frame[0]
if(nbytes != sizeof(frame[0]))
{
printf("Send Error frame[0]\n!");
break; //发送错误,退出
}
sleep(1);
nbytes = write(s, &frame[1], sizeof(frame[1])); //发送 frame[1]
if(nbytes != sizeof(frame[0]))
{
printf("Send Error frame[1]\n!");
break;
}
sleep(1);
}
close(s);
return 0;
}
CAN接收程序示例
/* 2. 报文过滤接收程序 */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <net/if.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <linux/can.h>
#include <linux/can/raw.h>
int main()
{
int s, nbytes;
struct sockaddr_can addr;
struct ifreq ifr;
struct can_frame frame;
struct can_filter rfilter[1];
s = socket(PF_CAN, SOCK_RAW, CAN_RAW); //创建套接字
strcpy(ifr.ifr_name, "can0" );
ioctl(s, SIOCGIFINDEX, &ifr); //指定 can0 设备
addr.can_family = AF_CAN;
addr.can_ifindex = ifr.ifr_ifindex;
bind(s, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, sizeof(addr)); //将套接字与 can0 绑定
//定义接收规则,只接收表示符等于 0x11 的报文
rfilter[0].can_id = 0x11;
rfilter[0].can_mask = CAN_SFF_MASK;
//设置过滤规则
setsockopt(s, SOL_CAN_RAW, CAN_RAW_FILTER, &rfilter, sizeof(rfilter));
while(1)
{
nbytes = read(s, &frame, sizeof(frame)); //接收报文
//显示报文
if(nbytes > 0)
{
printf(“ID=0x%X DLC=%d data[0]=0x%X\n”, frame.can_id,
frame.can_dlc, frame.data[0]);
}
}
close(s);
return 0;
}
¶ OpenCV
OpenCV(Open Source Computer Vision Library)是一个开源的计算机视觉和机器学习软件库。由一系列 C函数和少量 C++ 类构成,同时提供了 Python、Java、MATLAB 等语言的接口。
- 在使用OpenCV进行编程前,要先了解当前内置的OpenCV版本,使用下面命令可查询到版本
pkg-config --modversion opencv4
本系统默认内置版本为4.13.0。
- 创建工程目录
mkdir OpenCV_Demo
cd OpenCV_Demo
mkdir build image src
- 创建源文件
- CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8)
project( OpenCV_Demo )
find_package( OpenCV REQUIRED )
include_directories( ${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS} )
add_executable( image_demo src/image_demo.cpp )
add_executable( video_demo src/video_demo.cpp )
add_executable( camera_demo src/camera_demo.cpp )
target_link_libraries( image_demo ${OpenCV_LIBS} )
target_link_libraries( video_demo ${OpenCV_LIBS} )
target_link_libraries( camera_demo ${OpenCV_LIBS} )
- src/image_demo.cpp
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <iostream>
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
// 读取图片
cv::Mat image = cv::imread("../image/image.png");
// 确认图片读取成功
if(image.empty()) {
std::cerr << "Failed to open image file." << std::endl;
return -1;
}
//控制照片比例
resize(image, image, cv::Size(1280, 720));
// 显示图片
cv::imshow("Image with Box", image);
// 等待按键
cv::waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
- src/video_demo.cpp
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
int main() {
// 打开视频文件
VideoCapture cap("../image/video.mp4");
// 检查视频是否成功打开
if (!cap.isOpened()) {
std::cout << "Error opening video stream or file" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// 循环读取视频帧
while (true) {
Mat frame;
// 读取当前帧
cap >> frame;
// 检查是否成功读取帧
if (frame.empty())
break;
// 显示当前帧
imshow("Frame", frame);
// 按下 Esc 键退出循环
if (waitKey(25) == 27)
break;
}
// 释放VideoCapture对象和所有窗口
cap.release();
destroyAllWindows();
return 0;
}
- src/camera_demo.cpp
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main() {
// 打开默认摄像头
VideoCapture cap(41);
if (!cap.isOpened()) {
cout << "无法打开摄像头!" << endl;
return -1;
}
namedWindow("摄像头", WINDOW_NORMAL);
while (true) {
Mat frame;
cap >> frame;
// 显示视频帧
imshow("摄像头", frame);
// 按下空格键拍照
if (waitKey(30) == ' ')
{
// 生成文件名
time_t now = time(NULL);
tm *ltm = localtime(&now);
string filename = to_string(ltm->tm_year + 1900) + "-" + to_string(ltm->tm_mon + 1) + "-" + to_string(ltm->tm_mday) + "-" + to_string(ltm->tm_hour) + "-" + to_string(ltm->tm_min) + "-" + to_string(ltm->tm_sec) + ".jpg";
// 保存图片
imwrite(filename, frame);
cout << "已保存照片:" << filename << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
- 将自己的视频和图片放到image目录下,并分别命名为 image.png 和 video.mp4。这里的摄像头demo是使用USB摄像头作为示例。
- 编译
cd build
cmake ..
make
- 执行程序
./image_demo
./video_demo
./camera_demo

¶ MPP
- 查看 mpp 和 vpu 库版本
pkg-config --modversion rockchip_mpp
pkg-config --modversion rockchip_vpu
- 下载Rockchip mpp 源码库
git clone https://github.com/rockchip-linux/mpp.git
-
在下载的mpp目录里面 test目录,里面是一些mpp官方调用例程,用户可参考test目录和doc文档目录。
-
这里参考 test/mpi_dec_test.c 例程编写
vim mpp_dec_test.c
在官方例程中的头文件和在gcc编译时指定连接库。
源码如下
#define MODULE_TAG "mpp_dec_test"
#include <string.h>
#include <rockchip/rk_mpi.h>
#include <rockchip/mpp_mem.h>
#include <rockchip/mpp_env.h>
#include <rockchip/mpp_time.h>
#include <rockchip/mpp_common.h>
#include <rockchip/mpi_dec_utils.h>
typedef struct {
MpiDecTestCmd *cmd;
MppCtx ctx;
MppApi *mpi;
RK_U32 quiet;
/* end of stream flag when set quit the loop */
RK_U32 loop_end;
/* input and output */
DecBufMgr buf_mgr;
MppBufferGroup frm_grp;
MppPacket packet;
MppFrame frame;
FILE *fp_output;
RK_S32 frame_count;
RK_S32 frame_num;
RK_S64 first_pkt;
RK_S64 first_frm;
size_t max_usage;
float frame_rate;
RK_S64 elapsed_time;
RK_S64 delay;
FILE *fp_verify;
FrmCrc checkcrc;
} MpiDecLoopData;
static int dec_simple(MpiDecLoopData *data)
{
RK_U32 pkt_done = 0;
RK_U32 pkt_eos = 0;
MPP_RET ret = MPP_OK;
MpiDecTestCmd *cmd = data->cmd;
MppCtx ctx = data->ctx;
MppApi *mpi = data->mpi;
MppPacket packet = data->packet;
FileBufSlot *slot = NULL;
RK_U32 quiet = data->quiet;
FrmCrc *checkcrc = &data->checkcrc;
// when packet size is valid read the input binary file
ret = reader_read(cmd->reader, &slot);
mpp_assert(ret == MPP_OK);
mpp_assert(slot);
pkt_eos = slot->eos;
if (pkt_eos) {
if (data->frame_num < 0 || data->frame_num > data->frame_count) {
mpp_log_q(quiet, "%p loop again\n", ctx);
reader_rewind(cmd->reader);
pkt_eos = 0;
} else {
mpp_log_q(quiet, "%p found last packet\n", ctx);
data->loop_end = 1;
}
}
mpp_packet_set_data(packet, slot->data);
mpp_packet_set_size(packet, slot->size);
mpp_packet_set_pos(packet, slot->data);
mpp_packet_set_length(packet, slot->size);
// setup eos flag
if (pkt_eos)
mpp_packet_set_eos(packet);
do {
RK_U32 frm_eos = 0;
RK_S32 times = 30;
// send the packet first if packet is not done
if (!pkt_done) {
ret = mpi->decode_put_packet(ctx, packet);
if (MPP_OK == ret) {
pkt_done = 1;
if (!data->first_pkt)
data->first_pkt = mpp_time();
}
}
// then get all available frame and release
do {
RK_S32 get_frm = 0;
MppFrame frame = NULL;
try_again:
ret = mpi->decode_get_frame(ctx, &frame);
if (MPP_ERR_TIMEOUT == ret) {
if (times > 0) {
times--;
msleep(1);
goto try_again;
}
mpp_err("%p decode_get_frame failed too much time\n", ctx);
}
if (ret) {
mpp_err("%p decode_get_frame failed ret %d\n", ret, ctx);
break;
}
if (frame) {
if (mpp_frame_get_info_change(frame)) {
RK_U32 width = mpp_frame_get_width(frame);
RK_U32 height = mpp_frame_get_height(frame);
RK_U32 hor_stride = mpp_frame_get_hor_stride(frame);
RK_U32 ver_stride = mpp_frame_get_ver_stride(frame);
RK_U32 buf_size = mpp_frame_get_buf_size(frame);
MppBufferGroup grp = NULL;
mpp_log_q(quiet, "%p decode_get_frame get info changed found\n", ctx);
mpp_log_q(quiet, "%p decoder require buffer w:h [%d:%d] stride [%d:%d] buf_size %d",
ctx, width, height, hor_stride, ver_stride, buf_size);
if (MPP_FRAME_FMT_IS_FBC(cmd->format)) {
MppFrame frm = NULL;
mpp_frame_init(&frm);
mpp_frame_set_width(frm, width);
mpp_frame_set_height(frm, height);
mpp_frame_set_fmt(frm, cmd->format);
ret = mpi->control(ctx, MPP_DEC_SET_FRAME_INFO, frm);
mpp_frame_deinit(&frm);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("set fbc frame info failed\n");
break;
}
}
grp = dec_buf_mgr_setup(data->buf_mgr, buf_size, 24, cmd->buf_mode);
/* Set buffer to mpp decoder */
ret = mpi->control(ctx, MPP_DEC_SET_EXT_BUF_GROUP, grp);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("%p set buffer group failed ret %d\n", ctx, ret);
break;
}
data->frm_grp = grp;
/*
* All buffer group config done. Set info change ready to let
* decoder continue decoding
*/
ret = mpi->control(ctx, MPP_DEC_SET_INFO_CHANGE_READY, NULL);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("%p info change ready failed ret %d\n", ctx, ret);
break;
}
} else {
char log_buf[256];
RK_S32 log_size = sizeof(log_buf) - 1;
RK_S32 log_len = 0;
RK_U32 err_info = mpp_frame_get_errinfo(frame);
RK_U32 discard = mpp_frame_get_discard(frame);
if (!data->first_frm)
data->first_frm = mpp_time();
log_len += snprintf(log_buf + log_len, log_size - log_len,
"decode get frame %d", data->frame_count);
if (mpp_frame_has_meta(frame)) {
MppMeta meta = mpp_frame_get_meta(frame);
RK_S32 temporal_id = 0;
mpp_meta_get_s32(meta, KEY_TEMPORAL_ID, &temporal_id);
log_len += snprintf(log_buf + log_len, log_size - log_len,
" tid %d", temporal_id);
}
if (err_info || discard) {
log_len += snprintf(log_buf + log_len, log_size - log_len,
" err %x discard %x", err_info, discard);
}
mpp_log_q(quiet, "%p %s\n", ctx, log_buf);
data->frame_count++;
if (data->fp_output && !err_info)
dump_mpp_frame_to_file(frame, data->fp_output);
if (data->fp_verify) {
calc_frm_crc(frame, checkcrc);
write_frm_crc(data->fp_verify, checkcrc);
}
fps_calc_inc(cmd->fps);
}
frm_eos = mpp_frame_get_eos(frame);
mpp_frame_deinit(&frame);
get_frm = 1;
}
// try get runtime frame memory usage
if (data->frm_grp) {
size_t usage = mpp_buffer_group_usage(data->frm_grp);
if (usage > data->max_usage)
data->max_usage = usage;
}
// if last packet is send but last frame is not found continue
if (pkt_eos && pkt_done && !frm_eos) {
msleep(1);
continue;
}
if (frm_eos) {
mpp_log_q(quiet, "%p found last packet\n", ctx);
break;
}
if ((data->frame_num > 0 && (data->frame_count >= data->frame_num)) ||
((data->frame_num == 0) && frm_eos))
break;
if (get_frm)
continue;
break;
} while (1);
if ((data->frame_num > 0 && (data->frame_count >= data->frame_num)) ||
((data->frame_num == 0) && frm_eos)) {
data->loop_end = 1;
break;
}
if (pkt_done)
break;
/*
* why sleep here:
* mpi->decode_put_packet will failed when packet in internal queue is
* full,waiting the package is consumed .Usually hardware decode one
* frame which resolution is 1080p needs 2 ms,so here we sleep 1ms
* * is enough.
*/
msleep(1);
} while (1);
return ret;
}
static int dec_advanced(MpiDecLoopData *data)
{
MPP_RET ret = MPP_OK;
MpiDecTestCmd *cmd = data->cmd;
MppCtx ctx = data->ctx;
MppApi *mpi = data->mpi;
MppPacket packet = NULL;
MppPacket packet_ret = NULL;
MppFrame frame = data->frame;
MppFrame frame_ret = NULL;
MppMeta meta = NULL;
RK_U32 quiet = data->quiet;
FileBufSlot *slot = NULL;
FrmCrc *checkcrc = &data->checkcrc;
ret = reader_index_read(cmd->reader, 0, &slot);
mpp_assert(ret == MPP_OK);
mpp_assert(slot);
mpp_packet_init_with_buffer(&packet, slot->buf);
// setup eos flag
if (slot->eos)
mpp_packet_set_eos(packet);
/* use the MppFrame with prealloced buffer and do not release */
meta = mpp_packet_get_meta(packet);
if (meta)
mpp_meta_set_frame(meta, KEY_OUTPUT_FRAME, frame);
ret = mpi->decode_put_packet(ctx, packet);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("%p mpp decode put packet failed ret %d\n", ctx, ret);
data->loop_end = 1;
goto DONE;
}
if (!data->first_pkt)
data->first_pkt = mpp_time();
ret = mpi->decode_get_frame(ctx, &frame_ret);
if (ret || !frame_ret) {
mpp_err("%p mpp decode get frame failed ret %d frame %p\n", ctx, ret, frame_ret);
data->loop_end = 1;
goto DONE;
}
if (!data->first_frm)
data->first_frm = mpp_time();
if (frame_ret != frame)
mpp_err_f("mismatch frame %p -> %p\n", frame_ret, frame);
/* write frame to file here */
if (data->fp_output)
dump_mpp_frame_to_file(frame_ret, data->fp_output);
if (data->fp_verify) {
calc_frm_crc(frame_ret, checkcrc);
write_frm_crc(data->fp_verify, checkcrc);
}
mpp_log_q(quiet, "%p decoded frame %d\n", ctx, data->frame_count);
data->frame_count++;
if (mpp_frame_get_eos(frame_ret))
mpp_log_q(quiet, "%p found eos frame\n", ctx);
fps_calc_inc(cmd->fps);
meta = mpp_frame_get_meta(frame);
if (meta) {
ret = mpp_meta_get_packet(meta, KEY_INPUT_PACKET, &packet_ret);
if (ret || !packet_ret) {
mpp_err("%p mpp meta get packet failed ret %d\n", ctx, ret);
goto DONE;
}
if (packet_ret != packet)
mpp_err_f("mismatch packet %p -> %p\n", packet, packet_ret);
}
if (data->frame_num > 0) {
if (data->frame_count >= data->frame_num)
data->loop_end = 1;
} else if (data->frame_num == 0) {
if (slot->eos)
data->loop_end = 1;
}
DONE:
mpp_packet_deinit(&packet);
return ret;
}
void *thread_decode(void *arg)
{
MpiDecLoopData *data = (MpiDecLoopData *)arg;
MpiDecTestCmd *cmd = data->cmd;
MppCtx ctx = data->ctx;
MppApi *mpi = data->mpi;
RK_S64 t_s, t_e;
memset(&data->checkcrc, 0, sizeof(data->checkcrc));
data->checkcrc.luma.sum = mpp_malloc(RK_ULONG, 512);
data->checkcrc.chroma.sum = mpp_malloc(RK_ULONG, 512);
t_s = mpp_time();
if (cmd->simple) {
while (!data->loop_end)
dec_simple(data);
} else {
/* NOTE: change output format before jpeg decoding */
if (MPP_FRAME_FMT_IS_YUV(cmd->format) || MPP_FRAME_FMT_IS_RGB(cmd->format)) {
MPP_RET ret = mpi->control(ctx, MPP_DEC_SET_OUTPUT_FORMAT, &cmd->format);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("Failed to set output format 0x%x\n", cmd->format);
return NULL;
}
}
while (!data->loop_end)
dec_advanced(data);
}
t_e = mpp_time();
data->elapsed_time = t_e - t_s;
data->frame_rate = (float)data->frame_count * 1000000 / data->elapsed_time;
data->delay = data->first_frm - data->first_pkt;
mpp_log("decode %d frames time %lld ms delay %3d ms fps %3.2f\n",
data->frame_count, (RK_S64)(data->elapsed_time / 1000),
(RK_S32)(data->delay / 1000), data->frame_rate);
MPP_FREE(data->checkcrc.luma.sum);
MPP_FREE(data->checkcrc.chroma.sum);
return NULL;
}
int dec_decode(MpiDecTestCmd *cmd)
{
// base flow context
MppCtx ctx = NULL;
MppApi *mpi = NULL;
// input / output
MppPacket packet = NULL;
MppFrame frame = NULL;
// paramter for resource malloc
RK_U32 width = cmd->width;
RK_U32 height = cmd->height;
MppCodingType type = cmd->type;
// config for runtime mode
MppDecCfg cfg = NULL;
RK_U32 need_split = 1;
// resources
MppBuffer frm_buf = NULL;
pthread_t thd;
pthread_attr_t attr;
MpiDecLoopData data;
MPP_RET ret = MPP_OK;
mpp_log("mpi_dec_test start\n");
memset(&data, 0, sizeof(data));
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
cmd->simple = (cmd->type != MPP_VIDEO_CodingMJPEG) ? (1) : (0);
if (cmd->have_output) {
data.fp_output = fopen(cmd->file_output, "w+b");
if (NULL == data.fp_output) {
mpp_err("failed to open output file %s\n", cmd->file_output);
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
}
if (cmd->file_slt) {
data.fp_verify = fopen(cmd->file_slt, "wt");
if (!data.fp_verify)
mpp_err("failed to open verify file %s\n", cmd->file_slt);
}
ret = dec_buf_mgr_init(&data.buf_mgr);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("dec_buf_mgr_init failed\n");
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
if (cmd->simple) {
ret = mpp_packet_init(&packet, NULL, 0);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("mpp_packet_init failed\n");
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
} else {
RK_U32 hor_stride = MPP_ALIGN(width, 16);
RK_U32 ver_stride = MPP_ALIGN(height, 16);
ret = mpp_frame_init(&frame); /* output frame */
if (ret) {
mpp_err("mpp_frame_init failed\n");
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
data.frm_grp = dec_buf_mgr_setup(data.buf_mgr, hor_stride * ver_stride * 4, 4, cmd->buf_mode);
if (!data.frm_grp) {
mpp_err("failed to get buffer group for input frame ret %d\n", ret);
ret = MPP_NOK;
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
/*
* NOTE: For jpeg could have YUV420 and YUV422 the buffer should be
* larger for output. And the buffer dimension should align to 16.
* YUV420 buffer is 3/2 times of w*h.
* YUV422 buffer is 2 times of w*h.
* So create larger buffer with 2 times w*h.
*/
ret = mpp_buffer_get(data.frm_grp, &frm_buf, hor_stride * ver_stride * 4);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("failed to get buffer for input frame ret %d\n", ret);
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
mpp_frame_set_buffer(frame, frm_buf);
}
// decoder demo
ret = mpp_create(&ctx, &mpi);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("mpp_create failed\n");
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
mpp_log("%p mpi_dec_test decoder test start w %d h %d type %d\n",
ctx, width, height, type);
ret = mpp_init(ctx, MPP_CTX_DEC, type);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("%p mpp_init failed\n", ctx);
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
mpp_dec_cfg_init(&cfg);
/* get default config from decoder context */
ret = mpi->control(ctx, MPP_DEC_GET_CFG, cfg);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("%p failed to get decoder cfg ret %d\n", ctx, ret);
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
/*
* split_parse is to enable mpp internal frame spliter when the input
* packet is not aplited into frames.
*/
ret = mpp_dec_cfg_set_u32(cfg, "base:split_parse", need_split);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("%p failed to set split_parse ret %d\n", ctx, ret);
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
ret = mpi->control(ctx, MPP_DEC_SET_CFG, cfg);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("%p failed to set cfg %p ret %d\n", ctx, cfg, ret);
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
data.cmd = cmd;
data.ctx = ctx;
data.mpi = mpi;
data.loop_end = 0;
data.packet = packet;
data.frame = frame;
data.frame_count = 0;
data.frame_num = cmd->frame_num;
data.quiet = cmd->quiet;
pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_JOINABLE);
ret = pthread_create(&thd, &attr, thread_decode, &data);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("failed to create thread for input ret %d\n", ret);
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
if (cmd->frame_num < 0) {
// wait for input then quit decoding
mpp_log("*******************************************\n");
mpp_log("**** Press Enter to stop loop decoding ****\n");
mpp_log("*******************************************\n");
getc(stdin);
data.loop_end = 1;
}
pthread_join(thd, NULL);
cmd->max_usage = data.max_usage;
ret = mpi->reset(ctx);
if (ret) {
mpp_err("%p mpi->reset failed\n", ctx);
goto MPP_TEST_OUT;
}
MPP_TEST_OUT:
if (data.packet) {
mpp_packet_deinit(&data.packet);
data.packet = NULL;
}
if (frame) {
mpp_frame_deinit(&frame);
frame = NULL;
}
if (ctx) {
mpp_destroy(ctx);
ctx = NULL;
}
if (!cmd->simple) {
if (frm_buf) {
mpp_buffer_put(frm_buf);
frm_buf = NULL;
}
}
data.frm_grp = NULL;
if (data.buf_mgr) {
dec_buf_mgr_deinit(data.buf_mgr);
data.buf_mgr = NULL;
}
if (data.fp_output) {
fclose(data.fp_output);
data.fp_output = NULL;
}
if (data.fp_verify) {
fclose(data.fp_verify);
data.fp_verify = NULL;
}
if (cfg) {
mpp_dec_cfg_deinit(cfg);
cfg = NULL;
}
pthread_attr_destroy(&attr);
return ret;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
RK_S32 ret = 0;
MpiDecTestCmd cmd_ctx;
MpiDecTestCmd* cmd = &cmd_ctx;
memset((void*)cmd, 0, sizeof(*cmd));
cmd->format = MPP_FMT_BUTT;
cmd->pkt_size = MPI_DEC_STREAM_SIZE;
// parse the cmd option
ret = mpi_dec_test_cmd_init(cmd, argc, argv);
if (ret)
goto RET;
mpi_dec_test_cmd_options(cmd);
ret = dec_decode(cmd);
if (MPP_OK == ret)
mpp_log("test success max memory %.2f MB\n", cmd->max_usage / (float)(1 << 20));
else
mpp_err("test failed ret %d\n", ret);
RET:
mpi_dec_test_cmd_deinit(cmd);
return ret;
}
- 编译
gcc mpp_dec_test.c -o mpp_dec_test `pkg-config --cflags --libs rockchip_mpp rockchip_vpu` -lutils
- 运行
tail -f /var/log/syslog //开启新终端,监控输出
./mpp_dec_test -i /media/200frames_count.h264 -t 7 -n 200 -o ./decode.raw -w 640 -h 480
¶ QT
使用如下步骤安装Qt
sudo apt-get install build-essential
sudo apt-get install qtbase5-dev qtchooser qt5-qmake qtbase5-dev-tools
sudo apt-get install qtcreator
sudo apt-get install qt5*
¶ Electron
- 安装 Electron
sudo apt update
sudo apt install nodejs npm
npm install electron -D
- 项目初始化
mkdir my-electron-app && cd my-electron-app
npm init
- 修改package.json配置文件
vim package.json
{
"name": "my-electron-app",
"version": "1.0.0",
"main": "main.js",
"scripts": {
"start": "electron ."
},
"author": "9527",
"license": "ISC",
"description": "electron test",
"dependencies": {
"electron": "^31.2.0"
}
}
- 创建 main.js
vim main.js
console.log(123)
- 运行
npm start
¶ NPU
¶ 简介
RK3588 内置 NPU 模块, 处理性能最高可达6TOPS。使用该NPU需要下载RKNN SDK。RKNN SDK包括两套源码,一套是RKNN-Toolkit2,是用来将onnx模型转换为rknn模型。另一套为 RKNPU2。,是用来在板端进行推理。下面分别介绍这两套源码。
¶ PC端模型转换和推理 RKNN-Toolkit2
安装RKNN-Toolkit2有两种方法,通过pip install安装或者通过Docker镜像安装。
- 打开一个终端命令行窗口,安装Python3.6和pip3。
sudo apt-get install python3 python3-dev python3-pip
- 安装所需的依赖包。
sudo apt-get install libxslt1-dev zlib1g-dev libglib2.0 libsm6 libgl1-mesa-glx libprotobuf-dev gcc
- 下载
RKNN-Toolkit2工具
git clone https://github.com/airockchip/rknn-toolkit2.git
cd rknn-toolkit2
- 安装必要相应版本的依赖包。
pip3 install -r doc/requirements_cp36-1.5.2.txt
- 安装RKNN-Toolkit2(Python3.8 for x86_64)。
pip3 install packages/rknn_toolkit2-1.5.2+b642f30c-cp38-cp38-linux_x86_64.whl
目前安装的onnx会是最新的1.19.1版本,该版本会报错:AttributeError: module 'onnx' has no attribute 'mapping'
pip3 install onnx==1.18.0 onnxruntime==1.18.0
- 检查RKNN-Toolkit2 是否安装成功。
# 若没有出现错误,说明安装成功。同时按住Ctrl+D退出Python3。
python3
from rknn.api import RKNN
- 转换yolov5s_relu.onnx 为 rknn 模型并运行模型推理图片
cd examples/onnx/yolov5
python3 test.py
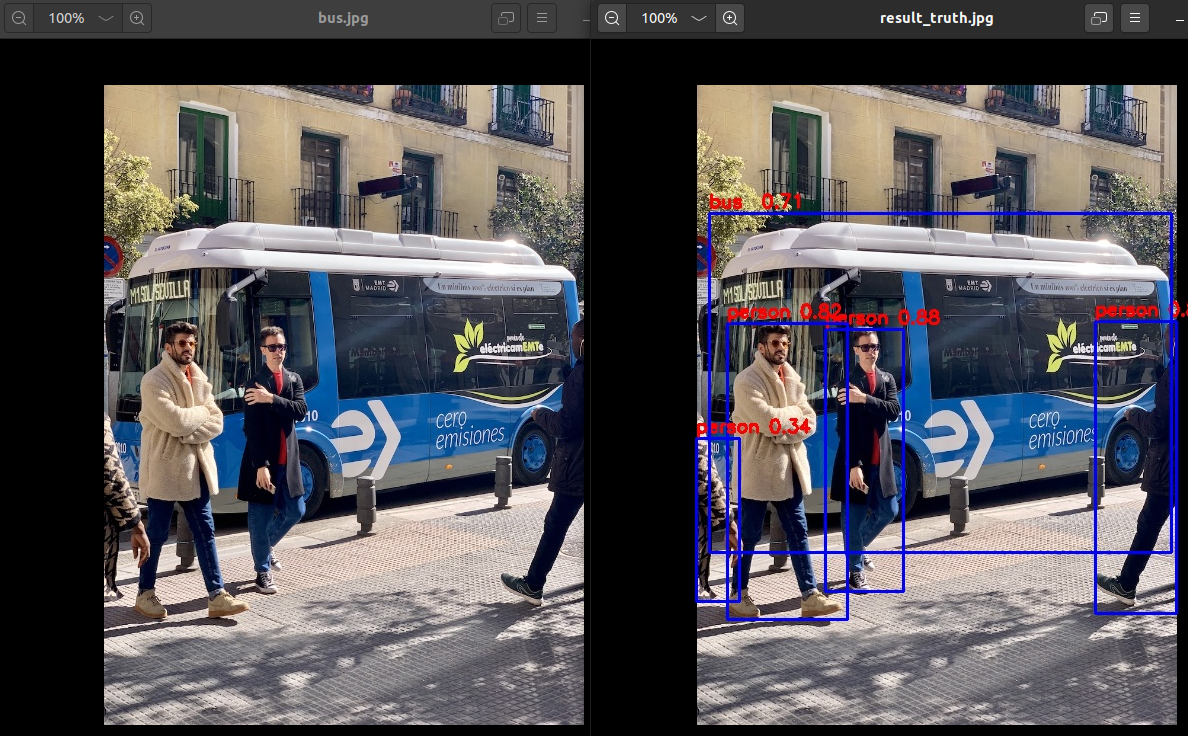
转换模型和推理脚本 test.py 运行成功后,转换后的模型默认保存路径为 examples/onnx/yolov5/yolov5s_relu.rknn , 推理的图片结果保存在 examples/onnx/yolov5/result.jpg 。
- 安装
Docker环境。
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu bionic stable"
sudo apt update
apt-cache policy docker-ce
sudo apt install docker-ce
sudo groupadd docker
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
sudo reboot
sudo systemctl status docker
- 下载
RKNN-Toolkit2工具
git clone https://github.com/airockchip/rknn-toolkit2.git
cd rknn-toolkit2
- 运行
Docker
cd docker/docker_full/
# 加载镜像
docker load --input rknn-toolkit2-1.5.2-cp36-docker.tar.gz
# 能查询到 REPOSITORY为 rknn-toolkit2,TAG为1.x.x-cp36则表示加载成功。
docker images
# 运行docker容器, 其中~/share/test/rknn-toolkit2-1.5.2/examples/onnx/yolov5为笔者的路径,读者需要修改为自己的路径。
docker run -t -i --privileged -v /dev/bus/usb:/dev/bus/usb -v ~/share/test/rknn-toolkit2-1.5.2/examples/onnx/yolov5:/rknn_yolov5_demo rknn-toolkit2:1.5.2-cp36 /bin/bash
cd rknn_yolov5_demo
# 转换yolov5s_relu.onnx 为 rknn 模型并行推理图片。
python3 ./test.py
# 退出 Docker
exit
转换模型和推理脚本 test.py 运行成功后,转换后的模型默认保存路径为 examples/onnx/yolov5/yolov5s_relu.rknn , 推理的图片结果保存在 examples/onnx/yolov5/result.jpg 。

¶ PC 连接板端推理
前面两种方式转换和推理模型均运行在PC端的模拟器环境中。本段是在上面两种的基础上,将推理环境修改为板端进行推理。
- 笔者的PC端是使用虚拟机搭建的
Ubuntu系统。需要安装ADB命令。读者的PC端是其他系统的话,请自行在网上搜索安装adb的方法。
sudo apt install adb
将开发板的 type-c 口连接到电脑 usb 口,在 PC端的Ubuntu系统 中输入以下命令,查看是否正常连接到开发板。
adb shell
exit
- 查看开发板的rknn服务是否运行。
adb shell pgrep rknn_server
如果没有进程号输出,表示rknn服务未运行。需要输入以下命令中其中一条即可。
adb shell
# 重启rknn服务
restart_rknn.sh
# 或者启动rknn服务
start_rknn.sh
exit
- 查看开发板的adb设备ID号
adb devices
这里笔者的开发板adb的id号是ca32be3b402e6579。
- 修改test.py脚本
打开 rknn-toolkit2/examples/onnx/yolov5/test.py
# 修改脚本target和device_id。 修改对应平台类型值(”rk3566”、”rk3568”、”rk3588”、”rv1103”、”rv1106”、”rk3562”)和设备ID,保存后再执行脚本生成适用于板子的模型并进行推理图片。
# 找到以下语句
rknn.config(mean_values=[[0, 0, 0]], std_values=[[255, 255, 255]], target_platform='rk3566')
...
ret = rknn.init_runtime()
# 修改为
rknn.config(mean_values=[[0, 0, 0]], std_values=[[255, 255, 255]], target_platform='rk3588')
...
ret = rknn.init_runtime(target='rk3588', device_id='ca32be3b402e6579')